The social hierarchy of Mesopotamia is a captivating topic that reveals the complexities of one of the world's earliest civilizations. This ancient society, often referred to as the "cradle of civilization," laid the foundations for modern social structures. In this article, we will explore the various layers of Mesopotamian society, their roles, and how these dynamics played a crucial part in the development of culture and governance in the region.
From the ruling elite to the laborers, each class in Mesopotamia had specific duties and privileges. Understanding this hierarchy is essential for appreciating the social, economic, and political frameworks that influenced daily life in ancient Mesopotamia. We will delve into the intricacies of this hierarchy, examining the distinctions between each class and how they interacted with one another.
Moreover, this exploration will highlight the significance of the social hierarchy in shaping Mesopotamian civilization, including its impact on art, religion, and governance. By the end of this article, you will have a clearer understanding of how the social hierarchy of Mesopotamia contributed to its legacy in human history.
Table of Contents
- Biography of Mesopotamian Society
- The Social Structure of Mesopotamia
- The Nobility Class
- The Role of Priests in Society
- The Merchant Class
- The Farmers and Laborers
- Understanding Slavery in Mesopotamia
- Conclusion
Biography of Mesopotamian Society
Mesopotamia, a region located between the Tigris and Euphrates rivers, is considered one of the first places where complex urban centers grew. Home to various cultures such as the Sumerians, Akkadians, Babylonians, and Assyrians, the society evolved over thousands of years.
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Location | Between the Tigris and Euphrates Rivers |
| Key Civilizations | Sumerians, Akkadians, Babylonians, Assyrians |
| Time Period | circa 3500 BC to 500 BC |
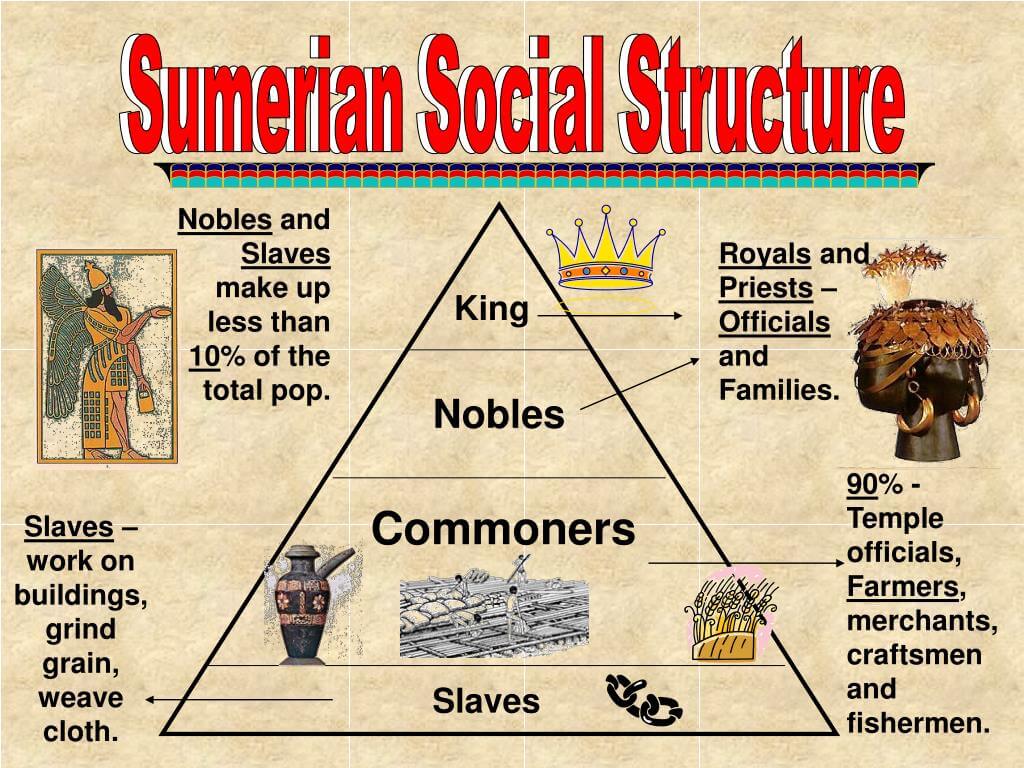
The Social Structure of Mesopotamia
The social hierarchy in Mesopotamia was structured in a way that allowed for clear divisions of labor, responsibilities, and privileges. This structure not only facilitated governance but also influenced the culture and economy of the region. The primary classes included:
- Nobility
- Priests
- Merchants
- Farmers and Laborers
- Slaves
The Nobility Class
The nobility class was at the top of the social hierarchy. This class included kings, governors, and other high-ranking officials who wielded significant power and influence. They were responsible for making laws, collecting taxes, and ensuring the welfare of their subjects. Nobles often owned vast lands and enjoyed various privileges:
- Access to education and resources
- Wealth and luxury
- Political power and influence
The Role of Priests in Society
Priests played a vital role in Mesopotamian society, acting as intermediaries between the gods and the people. Their responsibilities included conducting religious ceremonies, maintaining temples, and interpreting omens. The priestly class enjoyed high status and were often involved in political matters:
- Control over temple economies
- Influence in governance
- Education and literacy
The Merchant Class
Merchants in Mesopotamia were essential for trade and commerce, connecting different regions and facilitating the exchange of goods. This class included traders, artisans, and craftsmen who contributed to the economy through their skills and services. Merchants enjoyed several benefits:
- Wealth accumulation through trade
- Network building across regions
- Access to foreign goods and resources
The Farmers and Laborers
The majority of the population in Mesopotamia consisted of farmers and laborers. They worked the land and produced food, which was the backbone of the economy. Although they were lower in the social hierarchy, their work was crucial for the sustenance of society:
- Daily labor in agriculture
- Participation in local markets
- Community involvement and social cohesion
Understanding Slavery in Mesopotamia
Slavery existed in Mesopotamian society, although it was different from modern concepts of slavery. Slaves were often prisoners of war, debtors, or individuals who sold themselves into servitude. While they had limited rights, some could earn their freedom:
- Slaves performed various tasks, including household chores and agricultural work
- Some slaves were skilled workers and could gain respect
- Freedom was possible through various means, including payment or service
Conclusion
In conclusion, the social hierarchy of Mesopotamia was a complex system that shaped the lives of its people. From nobility and priests to merchants, farmers, and slaves, each class played a vital role in the development of this ancient civilization. Understanding these dynamics allows us to appreciate the rich history and cultural legacy of Mesopotamia.
We invite you to share your thoughts on the social hierarchy of Mesopotamia in the comments below. If you found this article informative, consider sharing it with others or exploring more articles on our site.
Thank you for reading, and we hope to see you again for more insightful discussions on historical topics!
Kelly Pegula Age: Uncovering The Life And Accomplishments Of An Outstanding Young Sportsman.
What Can We Know About Condoleezza Rice's Husband From Her Personal Life?
Nicolas Bardot: The Rising Star In The World Of Entertainment